Table of Contents
ToggleImagine walking through your favorite store and seeing a pair of shoes that not only fits perfectly but also comes with a virtual model strutting down the runway just for you. Welcome to the fascinating world of augmented displays! This technology isn’t just about flashy gadgets; it’s transforming how we interact with the world around us.
Overview of Augmented Display
Augmented displays create immersive visual experiences by overlaying digital information onto the real world. These systems utilize advanced technologies such as computer vision, simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), and display technologies. By combining these elements, augmented displays offer a seamless blend of digital content and physical surroundings.
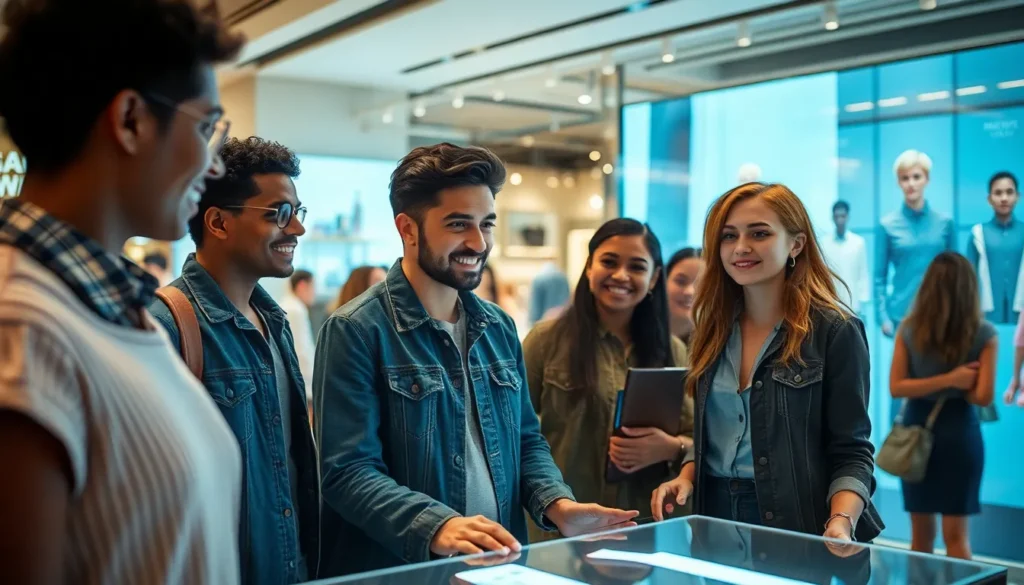
Retailers increasingly adopt augmented display technology to enhance customer engagement. Virtual fitting rooms serve as a prime example, allowing customers to see how clothing appears on their bodies without trying it on physically. Furthermore, interactive product displays give shoppers a deeper understanding of features and specifications.
In the education sector, augmented displays support interactive learning methods. Students access digital simulations that illustrate complex concepts, making learning more engaging and effective. Medical training also benefits, as augmented reality aids in visualizing anatomy during surgical simulations.
Users experience a variety of applications in different fields. For instance, engineers utilize augmented display technology for real-time data visualization of equipment during maintenance. Designers, on the other hand, find value in using augmented reality to visualize how furniture fits in physical spaces.
Overall, augmented displays foster innovative approaches to information presentation. They change how individuals interact with environments, creating opportunities for enhanced customer experiences, improved learning outcomes, and more effective operational processes. The technology’s expansion across various sectors signifies its growing importance in daily life.
Key Technologies Behind Augmented Display

Augmented display technology relies on several key components that enhance its functionality and user experience.
Display Technologies
Various display technologies underlie augmented displays, integrating digital and physical worlds. LCDs provide vibrant colors and clarity, enhancing visual immersion. OLED screens deliver deeper blacks and wider viewing angles, making images more lifelike. Projectors play a role by projecting digital content onto real-world surfaces, facilitating interactive environments. Holographic displays are emerging, offering advanced three-dimensional visuals that enable users to engage with content dynamically. These technologies work together to create seamless and impactful experiences, critical for applications in retail, education, and training.
Sensor Technologies
Sensor technologies form the backbone of augmented display systems. Cameras capture real-time images and track user movements, allowing for precise alignment of digital content with the physical environment. Depth sensors measure distances and create three-dimensional models, adding depth to the experience. Inertial measurement units track motion, helping to stabilize the digital overlays. GPS enhances outdoor experiences by providing location-based information. These sensors collaborate to ensure augmented displays accurately interpret the user’s surroundings, making interactions fluid and intuitive.
Applications of Augmented Display
Augmented display technology finds diverse applications across various sectors, enhancing daily interactions with digital information.
Industrial Uses
Manufacturing settings leverage augmented displays to streamline processes and improve safety. Workers utilize heads-up displays to view schematics and operational data without diverting their attention. Maintenance teams benefit from augmented overlays that highlight machinery specifications and maintenance schedules. In construction, crews access real-time project updates through augmented models that provide spatial understanding. These applications increase efficiency and reduce errors, promoting safer, more effective workflows.
Consumer Uses
Retail environments embrace augmented displays to elevate consumer experiences. Virtual fitting rooms allow customers to virtually try on clothing, eliminating the need for physical changing rooms. Enhanced product displays provide 3D visualizations and detailed information, helping shoppers make informed decisions. Consumers increasingly engage with interactive advertisements that enable product exploration before purchase. Enhanced buying experiences emerge within these immersive environments, creating greater customer satisfaction.
Healthcare Applications
Healthcare professionals incorporate augmented displays to improve training and patient care. Medical students utilize augmented simulations to learn anatomy and practice surgical techniques in lifelike scenarios. Surgeons access real-time data overlays during procedures, enhancing precision and decision-making. Patient education benefits as augmented displays illustrate complex medical conditions, aiding understanding. These applications contribute to a more informed approach to health management and advanced training methodologies.
Benefits of Augmented Display
Augmented displays offer significant advantages across various sectors. These benefits enhance user experiences, streamline operations, and contribute to improved outcomes.
Enhanced User Experience
Immersive experiences capture users’ attention and increase engagement. Virtual fitting rooms enable customers to visualize clothing on their bodies seamlessly. Interactive product displays provide instant access to relevant features, allowing informed decisions. Users report higher satisfaction levels with enhanced interactions. Educational simulations make complex topics more digestible, leading to increased knowledge retention. Augmented displays also foster creativity in artistic fields, inspiring unique design concepts through real-time visualization. With each advancement, users enjoy a more engaging relationship with technology.
Improved Efficiency
In many industries, augmented displays facilitate faster processes. Real-time data visualization supports engineers during equipment maintenance, reducing downtime. Heads-up displays enhance safety in industrial settings by overlaying critical information without distracting operators. In retail, interactive advertisements adjust to customer preferences, optimizing engagement. Healthcare professionals utilize augmented displays for training, improving surgical precision while lowering errors. Streamlined operations through augmented technology lead to better resource management and lower costs. These efficiencies illustrate how augmented displays reshape workflows across diverse applications.
Challenges and Limitations
Augmented displays face various challenges and limitations that can hinder their effectiveness and acceptance in different sectors.
Technical Challenges
Issues with hardware and software compatibility frequently arise in augmented display systems. Device limitations often restrict the performance of these technologies, leading to less immersive experiences. Latency in processing can disrupt real-time interactions, making it difficult for users to engage seamlessly with digital content. Ensuring reliable tracking in diverse environments also presents challenges, as lighting and movement can affect performance accuracy. Moreover, the complexity of integrating augmented display systems with existing infrastructure may slow down deployment efforts. Maintaining user privacy and security remains crucial, as augmented technologies continuously gather data from their surroundings.
Market Adoption
Market adoption of augmented displays encounters various hurdles. High costs associated with developing and implementing these solutions often deter businesses from investing. Limited consumer awareness and understanding of the technology can impact demand, resulting in slow growth rates. Moreover, organizations may hesitate because of uncertainty regarding return on investment. Regulatory concerns also contribute to the cautious approach, as businesses navigate compliance with privacy laws and safety standards. Additionally, competing technologies may lead to fragmentation, making it difficult for augmented displays to establish a dominant market position.
Augmented displays are revolutionizing the way people interact with digital information and their environments. By blending the physical and digital worlds, they offer immersive experiences that enhance engagement and understanding across various sectors. From retail to education and healthcare, the applications of this technology demonstrate its versatility and potential to improve user experiences.
Despite the challenges in adoption and implementation, the benefits of augmented displays are undeniable. As technology continues to evolve, it’s likely that augmented displays will become even more integral to everyday life. The ongoing advancements promise to unlock new opportunities for innovation and efficiency, ensuring that augmented displays remain at the forefront of technological progress.